This integration is powered by Singer's Heap tap and certified by Stitch. Check out and contribute to the repo on GitHub.
For support, contact Support.
Heap integration summary
Stitch’s Heap integration replicates data from Avro files published to Amazon S3 via Heap’s Connect for Amazon S3 feature. Refer to the Schema section for a list of objects available for replication.
Heap feature snapshot
A high-level look at Stitch's Heap (v1) integration, including release status, useful links, and the features supported in Stitch.
| STITCH | |||
| Release status |
Released on February 13, 2019 |
Supported by | |
| Stitch plan |
Standard |
API availability |
Available |
| Singer GitHub repository | |||
| REPLICATION SETTINGS | |||
| Anchor Scheduling |
Supported |
Advanced Scheduling |
Unsupported |
| Table-level reset |
Unsupported |
Configurable Replication Methods |
Unsupported |
| DATA SELECTION | |||
| Table selection |
Supported |
Column selection |
Supported |
| Select all |
Supported |
||
| TRANSPARENCY | |||
| Extraction Logs |
Supported |
Loading Reports |
Supported |
Connecting Heap
Heap setup requirements
To set up Heap in Stitch, you need:
-
Access to Heap Connect using Amazon S3. Stitch’s Heap integration currently only replicates data from Heap Amazon S3 instances.
-
Permissions in AWS Identity Access Management (IAM) that allow you to create policies, create roles, and attach policies to roles. This is required to grant Stitch authorization to your S3 bucket.
Step 1: Retrieve your Amazon Web Services account ID
- Sign into your Amazon Web Services (AWS) account.
- Click the user menu, located between the bell and Global menus in the top-right corner of the page.
- Click My Account.
-
In the Account Settings section of the page, locate the Account Id field:
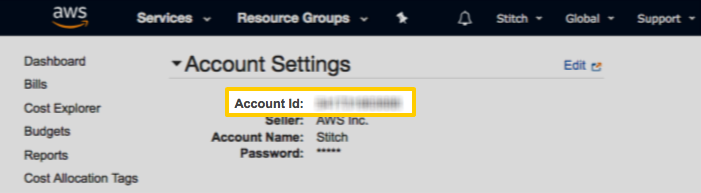
Keep this handy - you’ll need it to complete the setup.
Step 2: Add Heap as a Stitch data source
- Sign into your Stitch account.
-
On the Stitch Dashboard page, click the Add Integration button.
-
Click the Heap icon.
-
Enter a name for the integration. This is the name that will display on the Stitch Dashboard for the integration; it’ll also be used to create the schema in your destination.
For example, the name “Stitch Heap” would create a schema called
stitch_heapin the destination. Note: Schema names cannot be changed after you save the integration. - In the S3 Bucket field, enter the name of the bucket. Enter only the bucket name: No URLs,
https, or S3 parts. For example:heap-rs3-stitch-bucket - In the AWS Account ID field, paste the account ID you retrieve in Step 1.
Step 3: Define the historical replication start date
The Sync Historical Data setting defines the starting date for your Heap integration. This means that data equal to or newer than this date will be replicated to your data warehouse.
Change this setting if you want to replicate data beyond Heap’s default setting of 1 year. For a detailed look at historical replication jobs, check out the Syncing Historical SaaS Data guide.
Step 4: Create a replication schedule
In the Replication Frequency section, you’ll create the integration’s replication schedule. An integration’s replication schedule determines how often Stitch runs a replication job, and the time that job begins.
Heap integrations support the following replication scheduling methods:
To keep your row usage low, consider setting the integration to replicate less frequently. See the Understanding and Reducing Your Row Usage guide for tips on reducing your usage.
Step 5: Grant access to your bucket using AWS IAM
Next, Stitch will display a Configure Your Heap Integration page. This page contains the info you need to configure bucket access for Stitch, which is accomplished via an IAM policy and role.
Note: Saving the integration before you’ve completed the steps below will result in connection errors.
Step 5.1: Create an IAM policy
An IAM policy is JSON-based access policy language to manage permissions to Heap resources.
For more info about the permissions the auto-generated policy Stitch IAM policy grants, click the link below.
| Permission name | Operation | Description |
| s3:GetObject | GET Object |
Allows for the retrieval of objects from Amazon S3. |
| HEAD Object |
Allows for the retrieval of metadata from an object without returning the object itself. |
|
| s3:ListBucket | GET Bucket (List Objects) |
Allows for the return of some or all (up to 1,000) of the objects in a bucket. |
| HEAD Bucket |
Used to determine if a bucket exists and access is allowed. |
To create the IAM policy:
- In AWS, navigate to the IAM service by clicking the Services menu and typing IAM.
- Click IAM once it displays in the results.
- On the IAM home page, click Policies in the menu on the left side of the page.
- Click Create Policy.
- In the Create Policy page, click the JSON tab.
- Select everything currently in the text field and delete it.
- In the text field, paste the IAM policy from the Configure Your Heap Integration page in Stitch.
- Click Review policy.
- On the Review Policy page, give the policy a name. For example:
stitch_heap - Click Create policy.
Step 5.2: Create an IAM role for Stitch
Required permissions
To complete this step, you need the following AWS IAM permissions: CreateRole and AttachRolePolicy. Refer to Amazon’s documentation for more info.
Roles can’t be used for multiple integrations
If you’re creating multiple Heap integrations, you’ll need to complete this step for each integration you’re connecting.
The Role Name Stitch uses to connect to the Amazon resource is unique to the integration. Attempting to re-use a role for multiple integrations will cause connection errors.
In this step, you’ll create an IAM role for Stitch and apply the IAM policy from the previous step. This will ensure that Stitch is visible in any logs and audits.
To create the role, you’ll need the Account ID, External ID, and Role Name values provided on the Stitch Configure Your Heap Integration page.
- In AWS, navigate to the IAM Roles page.
- Click Create Role.
- On the Create Role page:
- In the Select type of trusted entity section, click the Another AWS account option.
- In the Account ID field, paste the Account ID from Stitch. Note: This isn’t your AWS account ID from Step 1 - this is the Account ID that displays in Stitch on the Configure Your Heap Integration page.
- In the Options section, check the Require external ID box.
- In the External ID field that displays, paste the External ID from the Stitch Configure Your Heap Integration page:
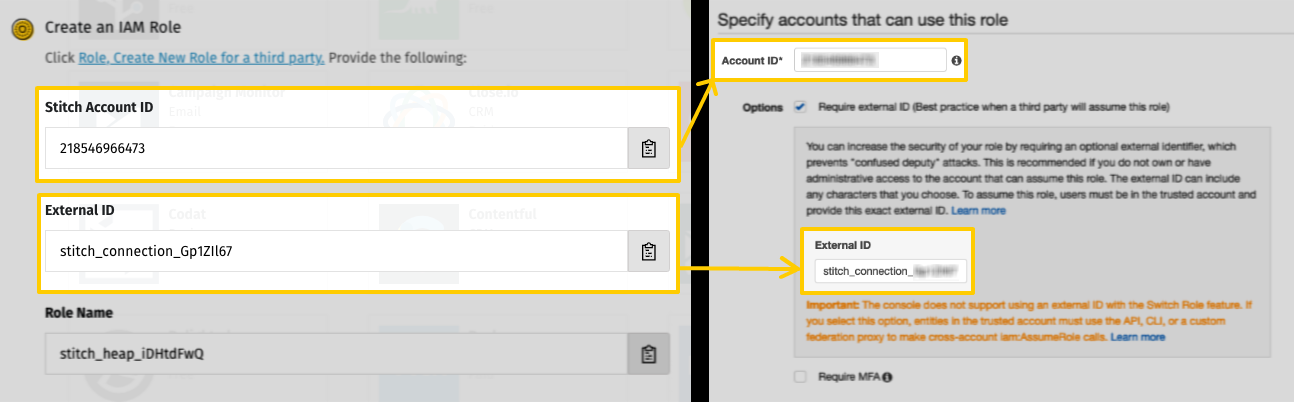
- Click Next: Permissions.
- On the Attach permissions page:
- Search for the policy you created in the previous step.
- Once located, check the box next to it in the table.
- Click Next: Tags.
- If you want to enter any tags, do so on the Add tags page. Otherwise, click Next: Review.
- On the Review page:
-
In the Role name field, paste the Role Name from the Stitch Configure Your Heap Integration page:
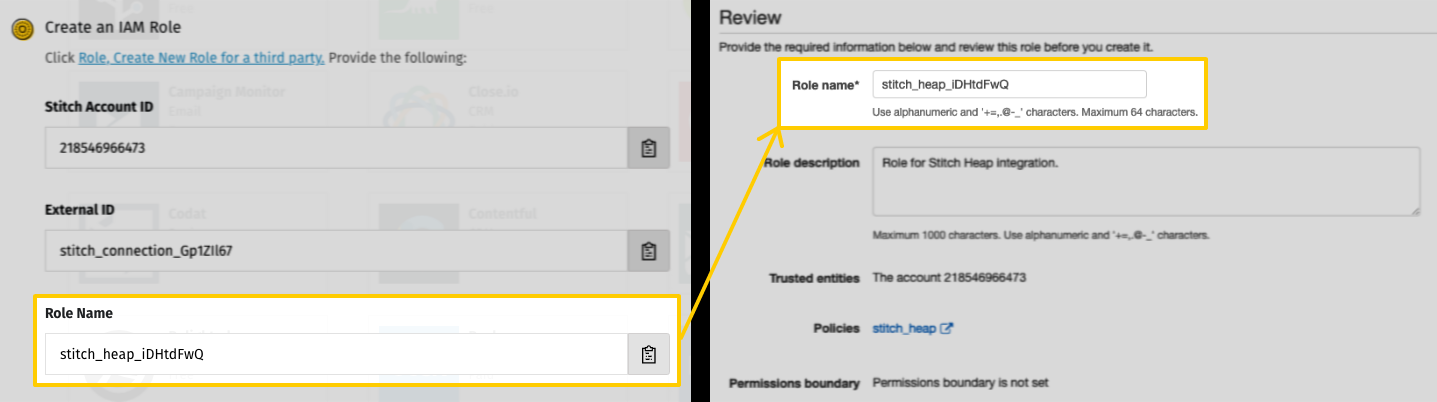
Remember: Role names are unique to the Stitch Heap integration they’re created for. Attempting to use the same role for multiple integrations will cause connection errors.
- Enter a description in the Role description field. For example:
Stitch role for Heap integration. - Click Create role.
-
Step 5.3: Check and save the connection in Stitch
After you’ve created the IAM policy and role, you can save the integration in Stitch. When finished, click Check and Save.
Step 6: Set objects to replicate
The last step is to select the tables and columns you want to replicate. Learn about the available tables for this integration.
Note: If a replication job is currently in progress, new selections won’t be used until the next job starts.
For Heap integrations, you can select:
-
Individual tables and columns
-
All tables and columns
Click the tabs to view instructions for each selection method.
- In the integration’s Tables to Replicate tab, locate a table you want to replicate.
-
To track a table, click the checkbox next to the table’s name. A blue checkmark means the table is set to replicate.
-
To track a column, click the checkbox next to the column’s name. A blue checkmark means the column is set to replicate.
- Repeat this process for all the tables and columns you want to replicate.
- When finished, click the Finalize Your Selections button at the bottom of the screen to save your selections.
- Click into the integration from the Stitch Dashboard page.
-
Click the Tables to Replicate tab.
- In the list of tables, click the box next to the Table Names column.
-
In the menu that displays, click Track all Tables and Fields:
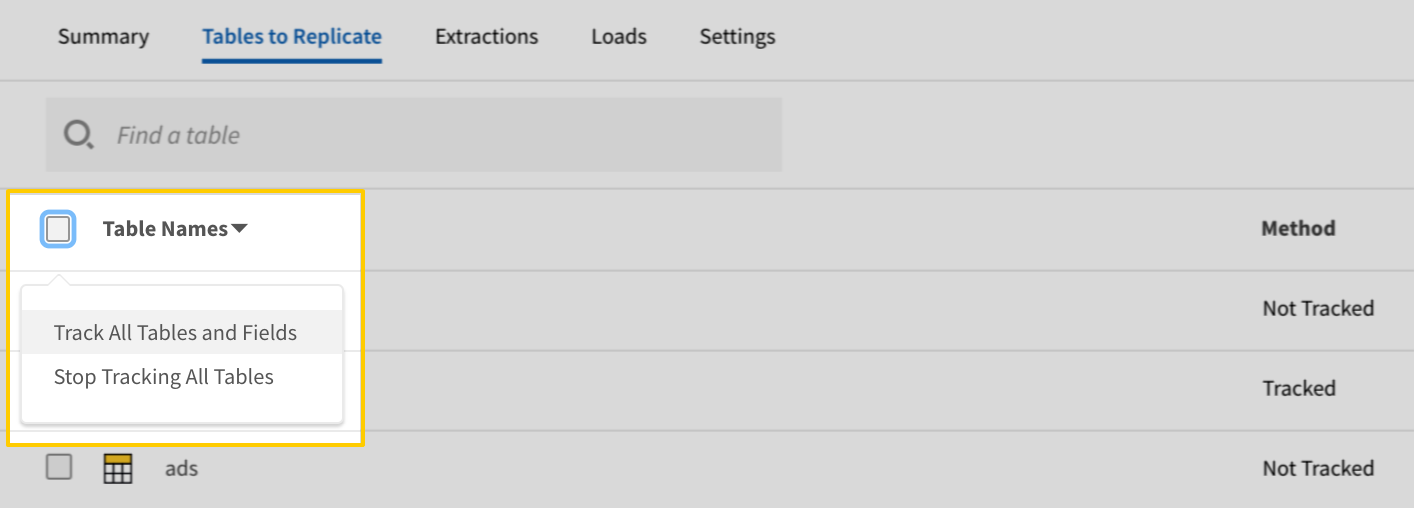
- Click the Finalize Your Selections button at the bottom of the page to save your data selections.
Initial and historical replication jobs
After you finish setting up Heap, its Sync Status may show as Pending on either the Stitch Dashboard or in the Integration Details page.
For a new integration, a Pending status indicates that Stitch is in the process of scheduling the initial replication job for the integration. This may take some time to complete.
Initial replication jobs with Anchor Scheduling
If using Anchor Scheduling, an initial replication job may not kick off immediately. This depends on the selected Replication Frequency and Anchor Time. Refer to the Anchor Scheduling documentation for more information.
Free historical data loads
The first seven days of replication, beginning when data is first replicated, are free. Rows replicated from the new integration during this time won’t count towards your quota. Stitch offers this as a way of testing new integrations, measuring usage, and ensuring historical data volumes don’t quickly consume your quota.
Heap replication
Replication in Stitch’s Heap integration depends on two factors:
- How Heap syncs data to your Amazon S3 bucket, and
- How Stitch identifies new data in Heap integrations
Heap data syncs to Amazon S3
Heap dumps data into Amazon S3 periodically. By default, this is on a nightly basis.
According to Heap’s documentation:
Heap will provide a periodic dump of data into S3 (nightly by default). Data will be delivered in the form of Avro-encoded files, each of which corresponds to one downstream table (though there can be multiple files per table). Dumps will be incremental, though individual table dumps can be full resyncs, depending on whether the table was recently toggled or the event definition modified.
This means that while files will only include new and updated data pertinent to that specific object (table), a full resync may be included.
Key-based Incremental Replication using file modification timestamps
To identify new and updated data for replication, Stitch will use file modification timestamps as Replication Keys and store them on a per-table basis. This means that only files dumped from a new Heap data sync will be selected for replication.
While data from Heap integrations is replicated using Key-based Incremental Replication, the behavior for this integration differs subtly from other integrations.
The table below compares Key-based Incremental Replication and Replication Key behavior for Heap to that of other integrations.
| Heap | Other integrations | |
| What's replicated during a replication job? |
The entire contents of a modified file. |
Only new or updated rows in a table. |
| What's used as a Replication Key? |
The time a file is modified. |
A column or columns in a table. |
| Are Replication Keys inclusive? |
No. Only files with a modification timestamp value greater than the last saved bookmark are replicated. |
Yes. Rows with a Replication Key value greater than or equal to the last saved bookmark are replicated. |
Heap table reference
Schemas and versioning
Schemas and naming conventions can change from version to version, so we recommend verifying your integration’s version before continuing.
The schema and info displayed below is for version 1 of this integration.
This is the latest version of the Heap integration.
Custom attributes
Heap’s data model is dynamic, meaning it changes as custom attributes are added to object types in your account. For example: Adding new user attributes to the user object.
This means that the Heap schema in your destination may also change over time as you add new attributes in Heap.
When a new attribute is added to an object in Heap, it will display as a selectable field in the Stitch app. Note: To include the field in replication, you’ll need to select it in Stitch. Stitch will not automatically select new fields.
The schema documentation following this section outlines the default attributes for each object type according to Heap’s documentation.
Event tables
For each event type you define in Heap, a table for that event will be available for selection in Stitch.
For example: If there’s a Sign up - Click button event, there will be a table named sign_up_click_button.
Refer to the [event_type] schema documentation for a list of default event attributes.
Note: When new event types are added in Heap, you will need to select the table and fields in Stitch to include it in replication.
Table and column names in your destination
Depending on your destination, table and column names may not appear as they are outlined below.
For example: Object names are lowercased in Redshift (CusTomERs > customers), while case is maintained in PostgreSQL destinations (CusTomERs > CusTomERs). Refer to the Loading Guide for your destination for more info.
event_tables
For every event type defined in Heap, a table will display in the Stitch app. The name of the table will be the event name, which Heap will first strip the non-alphanumeric characters from. For example: The table name for Sign Up - Click Link will be transformed into sign_up_click_link by Heap.
Note: Custom attributes are supported for this table. As Heap schemas are dynamic, Stitch’s event_tables documentation will only list the non-custom attributes outlined in Heap’s documentation.
|
Key-based Incremental |
|
|
Primary Key |
event_id |
| Useful links |
| Join event_tables with | on |
|---|---|
| pageviews |
event_tables.event_id = pageviews.event_id event_tables.session_id = pageviews.session_id event_tables.user_id = pageviews.user_id |
| sessions |
event_tables.event_id = sessions.event_id event_tables.session_id = sessions.session_id event_tables.user_id = sessions.user_id |
| user_migrations |
event_tables.user_id = user_migrations.to_user_id |
| users |
event_tables.user_id = users.user_id |
|
IP STRING |
|
action_method STRING |
|
app_name STRING |
|
app_version STRING |
|
browser STRING |
|
carrier STRING |
|
city STRING |
|
country STRING |
|
device STRING |
|
device_type STRING |
|
event_id
STRING |
|
hash STRING |
|
href STRING |
|
landing_page STRING |
|
library STRING |
|
path STRING |
|
platform STRING |
|
query STRING |
|
referrer STRING |
|
region STRING |
|
screen_ally_id STRING |
|
screen_ally_label STRING |
|
search_keyword STRING |
|
session_id INTEGER |
|
session_time STRING |
|
target_ally_id STRING |
|
target_ally_label STRING |
|
target_text STRING |
|
target_view_class STRING |
|
target_view_name STRING |
|
time STRING |
|
title STRING |
|
type STRING |
|
user_id INTEGER |
|
utm_campaign STRING |
|
utm_content STRING |
|
utm_medium STRING |
|
utm_source STRING |
|
utm_term STRING |
|
view_controller STRING |
pageviews
The pageviews table contains info about pageviews.
Note: Custom attributes are supported for this table. As Heap schemas are dynamic, Stitch’s pageviews documentation will only list the non-custom attributes outlined in Heap’s documentation.
|
Key-based Incremental |
|
|
Primary Key |
event_id |
| Useful links |
| Join pageviews with | on |
|---|---|
| event_tables |
pageviews.event_id = event_tables.event_id pageviews.session_id = event_tables.session_id pageviews.user_id = event_tables.user_id |
| sessions |
pageviews.event_id = sessions.event_id pageviews.session_id = sessions.session_id pageviews.user_id = sessions.user_id |
| user_migrations |
pageviews.user_id = user_migrations.to_user_id |
| users |
pageviews.user_id = users.user_id |
|
IP STRING |
|
app_name STRING |
|
app_version STRING |
|
browser STRING |
|
carrier STRING |
|
city STRING |
|
country STRING |
|
device STRING |
|
device_type STRING |
|
event_id
STRING |
|
hash STRING |
|
landing_page STRING |
|
library STRING |
|
path STRING |
|
platform STRING |
|
query STRING |
|
referrer STRING |
|
region STRING |
|
screen_ally_id STRING |
|
screen_ally_label STRING |
|
search_keyword STRING |
|
session_id INTEGER |
|
session_time STRING |
|
time STRING |
|
title STRING |
|
user_id INTEGER |
|
utm_campaign STRING |
|
utm_content STRING |
|
utm_medium STRING |
|
utm_source STRING |
|
utm_term STRING |
|
view_controller STRING |
sessions
The sessions table contains info about sessions. In Heap, a web session ends after 30 minutes of user inactivity, while in iOS, a session ends after the app has entered the background.
Note: Custom attributes are supported for this table. As Heap schemas are dynamic, Stitch’s sessions documentation will only list the non-custom attributes outlined in Heap’s documentation.
|
Key-based Incremental |
|
|
Primary Key |
event_id |
| Useful links |
| Join sessions with | on |
|---|---|
| event_tables |
sessions.event_id = event_tables.event_id sessions.session_id = event_tables.session_id sessions.user_id = event_tables.user_id |
| pageviews |
sessions.event_id = pageviews.event_id sessions.session_id = pageviews.session_id sessions.user_id = pageviews.user_id |
| user_migrations |
sessions.user_id = user_migrations.to_user_id |
| users |
sessions.user_id = users.user_id |
|
IP STRING |
|
app_name STRING |
|
app_version STRING |
|
browser STRING |
|
carrier STRING |
|
city STRING |
|
country STRING |
|
device STRING |
|
device_type STRING |
|
event_id
STRING |
|
landing_page STRING |
|
library STRING |
|
platform STRING |
|
referrer STRING |
|
region STRING |
|
search_keyword STRING |
|
session_id INTEGER |
|
time STRING |
|
user_id INTEGER |
|
utm_campaign STRING |
|
utm_content STRING |
|
utm_medium STRING |
|
utm_source STRING |
|
utm_term STRING |
user_migrations
The user_migrations table contains info about user migrations.
Note: Custom attributes are supported for this table. As Heap schemas are dynamic, Stitch’s user_migrations documentation will only list the non-custom attributes outlined in Heap’s documentation.
|
Key-based Incremental |
|
|
Primary Key |
from_user_id |
| Useful links |
| Join user_migrations with | on |
|---|---|
| event_tables |
user_migrations.to_user_id = event_tables.user_id |
| pageviews |
user_migrations.to_user_id = pageviews.user_id |
| sessions |
user_migrations.to_user_id = sessions.user_id |
| users |
user_migrations.to_user_id = users.user_id |
|
from_user_id
STRING |
|
time STRING |
|
to_user_id INTEGER |
users
The users table contains info about users.
Note: Custom attributes are supported for this table. As Heap schemas are dynamic, Stitch’s users documentation will only list the non-custom attributes outlined in Heap’s documentation.
|
Key-based Incremental |
|
|
Primary Key |
user_id |
| Useful links |
| Join users with | on |
|---|---|
| event_tables |
users.user_id = event_tables.user_id |
| pageviews |
users.user_id = pageviews.user_id |
| sessions |
users.user_id = sessions.user_id |
| user_migrations |
users.user_id = user_migrations.to_user_id |
|
STRING |
|
handle STRING |
|
identity STRING |
|
joindate STRING |
|
last_modified STRING |
|
user_id
STRING |
| Related | Troubleshooting |
Questions? Feedback?
Did this article help? If you have questions or feedback, feel free to submit a pull request with your suggestions, open an issue on GitHub, or reach out to us.