This integration is powered by Singer's Google CloudSQL MySQL tap and certified by Stitch. Check out and contribute to the repo on GitHub.
For support, contact Support.
Google CloudSQL MySQL feature snapshot
A high-level look at Stitch's Google CloudSQL MySQL (v1) integration, including release status, useful links, and the features supported in Stitch.
| STITCH | |||
| Release status |
Deprecated on November 8, 2021 |
Supported by | |
| Stitch plan |
Standard |
Supported versions |
n/a |
| API availability |
Not available |
Singer GitHub repository | |
| CONNECTION METHODS | |||
| SSH connections |
Unsupported |
SSL connections |
Unsupported |
| REPLICATION SETTINGS | |||
| Anchor Scheduling |
Supported |
Advanced Scheduling |
Supported |
| Table-level reset |
Supported |
Configurable Replication Methods |
Supported |
| REPLICATION METHODS | |||
| Log-based Replication |
Supported |
Key-based Replication |
Supported |
| Full Table Replication |
Supported |
||
| DATA SELECTION | |||
| Table selection |
Supported |
Column selection |
Supported |
| View replication |
Supported |
Select all |
Supported, with prerequisites |
| TRANSPARENCY | |||
| Extraction Logs |
Supported |
Loading Reports |
Supported |
Connecting Google CloudSQL MySQL
Google CloudSQL MySQL setup requirements
To set up Google CloudSQL MySQL in Stitch, you need:
-
Permissions in Google Cloud that allow you to modify the database’s connection settings. This is required to whitelist Stitch’s IP addresses.
-
The
CREATE USERorINSERTprivilege (for themysqldatabase). TheCREATE USERprivilege is required to create a database user for Stitch. -
The
GRANT OPTIONprivilege. TheGRANT OPTIONprivilege is required to grant the necessary privileges to the Stitch database user. -
If using Log-based Replication, you’ll need:
- A database running MySQL 5.6.2 or greater Earlier versions of MySQL do not include binlog replication functionality, which is required for Log-based Replication.
- To connect to the master instance. Google doesn’t currently support binlog replication on read replicas.
Step 1: Verify your Stitch account's data pipeline region
First, you’ll log into Stitch and verify the data pipeline region your account is using. Later in this guide, you’ll need to grant Stitch access by whitelisting our IP addresses.
The IP addresses you’ll whitelist depend on the Data pipeline region your account is in.
- Sign into your Stitch account, if you haven’t already.
- Click User menu (your icon) > Edit User Settings and locate the Data pipeline region section to verify your account’s region.
-
Locate the list of IP addresses for your region:
Keep this list handy - you’ll need it later.
Step 2: Configure database connection settings
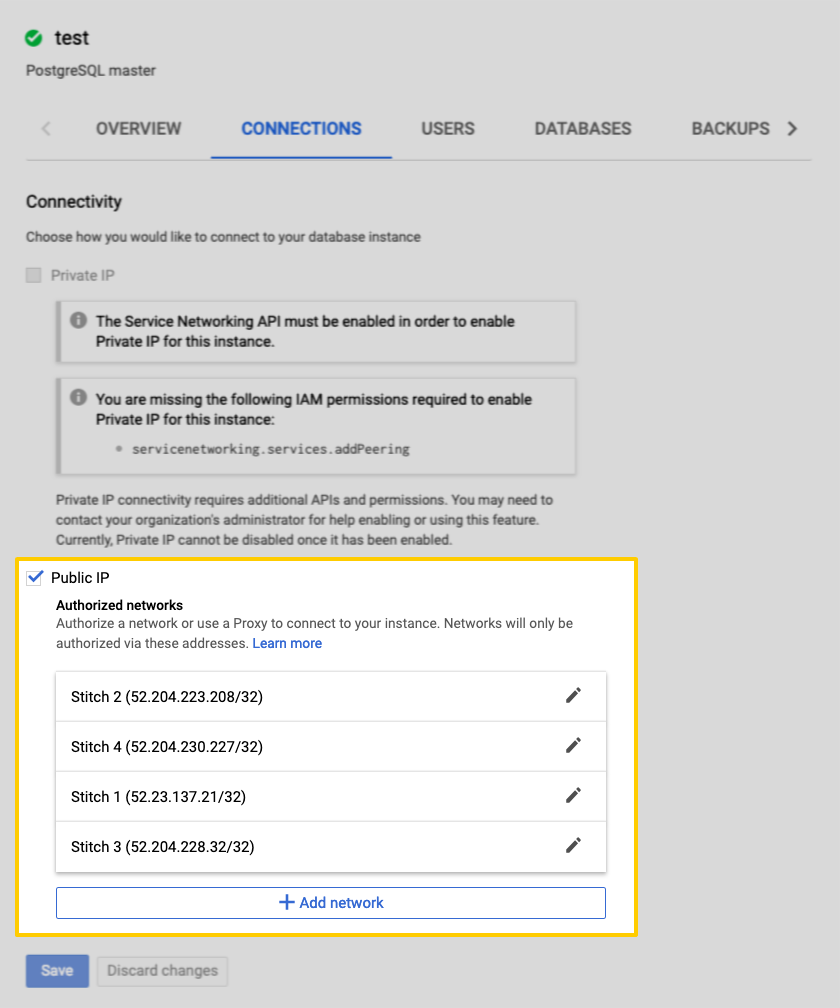
For Stitch to successfully connect with your CloudSQL instance, you’ll need to add our IP addresses to the database’s authorized networks list.
- Sign into your Google Cloud Platform account.
- Navigate to the Cloud SQL Instances page.
- Click the instance name to open its details page.
- Click the Connections tab.
- Locate the Public IP section.
-
For each of the Stitch data pipeline region IP addresses you retrieved in Step 1, complete the following:
- Click + Add network.
- In the Name field, enter a name for the IP address. For example:
Stitch 1for the first IP address,Stitch 2for the second, and so on. - In the Network field, paste one of the IP addresses for your Stitch data pipeline region that you retrieved in Step 1.
- Click Done.
- Repeat these steps until all of Stitch’s IP addresses for your data pipeline region have been added.
- When finished, click Save to update the instance.
Step 3: Configure Log-based Incremental Replication
Important: Requirements for configuring binlog replication
To use binlog replication, your Google CloudSQL MySQL database must be running MySQL version 5.6.2 or greater.
Additionally, setting up binlog replication requires rebooting your database to ensure parameter changes take effect. To minimize disruptions, we recommend performing the reboot during non-peak usage hours.
While Log-based Incremental Replication is the most accurate and efficient method of replication, using this replication method may, at times, require manual intervention or impact the source database’s performance. Refer to the Log-based Incremental Replication documentation for more info.
You can also use one of Stitch’s other Replication Methods, which don’t require any database configuration. Replication Methods can be changed at any time.
Step 3.1: Enable automated backups and binary logging
In this step, you’ll enable automated backups and binary logging for the Google CloudSQL MySQL database. This is required to use Log-based Incremental Replication.

- On the Instance details page in Google Cloud Platform, click the Edit option at the top of the page.
- In the Configuration options section, open Enable auto backups.
-
If unchecked, check the Automate backups option and select a window for automated backups.
Note: This is required to use Log-based Incremental Replication.
- If unchecked, check the Enable binary logging option.
- Click Save.
When binary logging is enabled, Google Cloud SQL will define the required server settings using their pre-defined defaults. Refer to the Server settings list tab for explanations of these parameters and their default values. No other configuration is required on your part.
In the table below are the names, required values, and descriptions of the server settings you must define.
| Setting | Value | Description |
Step 3.2: Retrieve server IDs
Required for Log-based Replication
This step is required if using Log-based Replication and any of the following are true:
- You’re connecting a read replica to Stitch
- You’re connecting multiple databases to Stitch, all of which are on the same Google CloudSQL MySQL server. These can be read replicas, or databases on the master instance.
- You’re adding a new Google CloudSQL MySQL Stitch integration, and the database is on the same server as other previously-connected databases.
When Stitch connects to your database and uses Log-based Replication, a unique server ID will be required. This ID ensures that the integration - or integrations, if you’re connecting multiple databases - will not encounter conflicts during the replication process.
To avoid conflicts, you’ll check which server IDs are currently in use and then define a new, unqiue ID in Stitch.
- Log into the MySQL server that acts as the replication master.
-
Run the following statement:
mysql> SHOW SLAVE HOSTS; -
The
SHOW SLAVE HOSTSstatement will return information about servers that are or have been connected as replication slaves:+------------+-------------+------+-----------+------------+ | Server_id | Host | Port | Master_id | Slave_UUID | +------------+-------------+------+-----------+------------+ | 192168010 | stitch_prod | 3306 | 192168011 | <UUID> | | 1921680101 | stitch_dev | 3306 | 192168011 | <UUID> | +------------+-------------+------+-----------+------------+
When you complete the setup in Stitch, you’ll define a unique server ID for your Stitch Google CloudSQL MySQL integration to use.
Step 4: Create a Stitch database user
CREATE USER and GRANT OPTION privileges to complete this step.
Next, you’ll create a dedicated database user for Stitch. This will ensure Stitch is visible in any logs or audits, and allow you to maintain your privilege hierarchy.
- Log into your database as a user with
CREATE USERandGRANT OPTIONprivileges. -
Run the following command to create the Stitch database user:
CREATE USER '<stitch_username>'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '<password>';Replace
<password>with a secure password. -
Grant the Stitch user
SELECTprivileges by running this command for every table you want to replicate:GRANT SELECT ON '<database_name>'.'<table_name>' to '<stitch_username>'@'localhost';Limiting access to only the tables you want to replicate ensures that the integration can complete discovery (a structure sync) in a timely manner. If you encounter issues in Stitch where tables aren’t displaying, try limiting the Stitch database user’s table access.
Note: Column-level permissions are not supported for use with Log-based Incremental Replication. Restricting access to columns will cause replication issues.
Important: Using Log-based Incremental Replication
Additionally, if you want to use Log-based Incremental Replication, you’ll also need to grant the Stitch user replication privileges:
GRANT REPLICATION CLIENT, REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO '<stitch_username>'@'localhost';
See the Privileges list tab for an explanation of why these permissions are required by Stitch.
In the table below are the database user privileges Stitch requires to connect to and replicate data from a Google CloudSQL MySQL database.
| Privilege name | Reason for requirement |
| SELECT |
Required to select rows from tables in a database. |
| REPLICATION CLIENT |
Required for binlog replication. Required to use |
| REPLICATION SLAVE |
Required for binlog replication. Required to use |
Step 5: Connect Stitch
In this step, you’ll complete the setup by entering the database’s connection details and defining replication settings in Stitch.
Step 5.1: Locate the database connection details in Google
In this step, you’ll locate the Google CloudSQL MySQL database’s IP address in the Google Cloud Platform console. This will be used to complete the setup in Stitch.
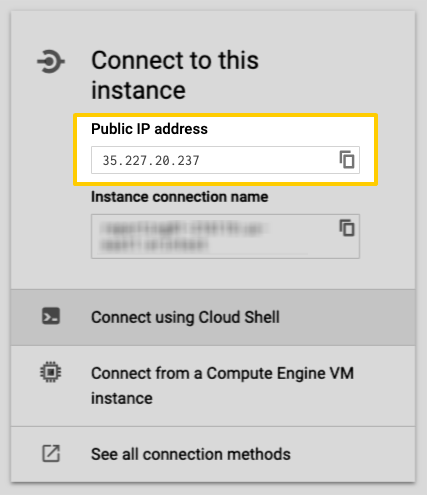
In this step, you’ll locate the Google CloudSQL MySQL database’s public IP address in the Google Cloud Platform console. This will be used to complete the setup in Stitch.
- In the CloudSQL Instances page, locate the instance you want to connect to Stitch.
- When the instance’s Overview page displays, scroll down to the Connect to this instance section.
- Locate the Public IP address field.
- Copy and paste the public IP address into a text file or leave this page open and open your Stitch account in another tab.
Step 5.2: Define the database connection details in Stitch
- If you aren’t signed into your Stitch account, sign in now.
-
On the Stitch Dashboard page, click the Add Integration button.
- Locate and click the Google CloudSQL MySQL icon.
-
Fill in the fields as follows:
-
Integration Name: Enter a name for the integration. This is the name that will display on the Stitch Dashboard for the integration; it’ll also be used to create the schema in your destination.
For example, the name “Stitch Google CloudSQL MySQL” would create a schema called
stitch_google_cloudsql_mysqlin the destination. Note: The schema name cannot be changed after the integration is saved. -
Integration Name: Enter the host address (endpoint) of your Google CloudSQL MySQL instance. This will be the value of the Public IP address that you retrieved in the previous step.
-
Port: Enter the port used by the Google CloudSQL MySQL instance. The default is
3306. -
Username: Enter the Stitch Google CloudSQL MySQL database user’s username.
-
Password: Enter the password for the Stitch Google CloudSQL MySQL database user.
-
Server ID: Optional: Enter the unique server ID of instance you’re connecting to Stitch.
This can be any numeric value within MySQL’s accepted server ID range, as long as it’s unique to the instance. For example: If in the Retrieve Server IDs step there are servers with the IDs
192168010and1921680101, you can enter any other numbers in this field.
-
Step 5.3: Define the Log-based Replication setting
In the Log-based Replication section, you can set this as the integration’s default Replication Method.
When enabled, tables that are set to replicate will use Log-based Incremental Replication by default. If you don’t want a table to use Log-based Incremental Replication, you can change it in the Table Settings page for that table.
If this setting isn’t enabled, you’ll have to select a Replication Method for each table you set to replicate.
Step 5.4: Create a replication schedule
In the Replication Frequency section, you’ll create the integration’s replication schedule. An integration’s replication schedule determines how often Stitch runs a replication job, and the time that job begins.
Google CloudSQL MySQL integrations support the following replication scheduling methods:
-
Advanced Scheduling using Cron (Advanced or Premium plans only)
To keep your row usage low, consider setting the integration to replicate less frequently. See the Understanding and Reducing Your Row Usage guide for tips on reducing your usage.
Step 5.5: Save the integration
When finished, click Check and Save.
Stitch will perform a connection test to the Google CloudSQL MySQL database; if successful, a Success! message will display at the top of the screen. Note: This test may take a few minutes to complete.
Step 6: Select data to replicate
The last step is to select the tables and columns you want to replicate.
Note: If a replication job is currently in progress, new selections won’t be used until the next job starts.
For Google CloudSQL MySQL integrations, you can select:
-
Individual tables and columns
-
All tables and columns (except views)
-
Database views
Click the tabs to view instructions for each selection method.
- In the Integration Details page, click the Tables to Replicate tab.
- Locate a table you want to replicate.
-
Click the checkbox next to the table’s name. A blue checkmark means the table is set to replicate.
-
After you set a table to replicate, a page with the table’s columns will display. De-select columns if needed.
- Next, you’ll define the table’s Replication Method. Click the Table Settings button.
- In the Table Settings page:
-
Define the table’s Replication Method, or skip this step if you want to use the integration’s default method.
-
If using Key-based Incremental Replication, select a Replication Key.
-
When finished, click Update Settings.
-
-
Repeat this process for every table you want to replicate.
- Click the Finalize Your Selections button at the bottom of the page to save your data selections.
Important: Before using this feature, note that:
-
Using the Select All feature will overwrite any previous selections. However, selections aren’t final until Finalize Your Selections is clicked. Clicking Cancel will restore your previous selections.
-
Log-based Incremental Replication must be enabled and set as the default Replication Method to use the Select All feature.
Refer to the Select All guide for more info about this feature.
- Click into the integration from the Stitch Dashboard page.
-
Click the Tables to Replicate tab.
-
Navigate to the table level, selecting any databases and/or schemas that contain tables you want to replicate.
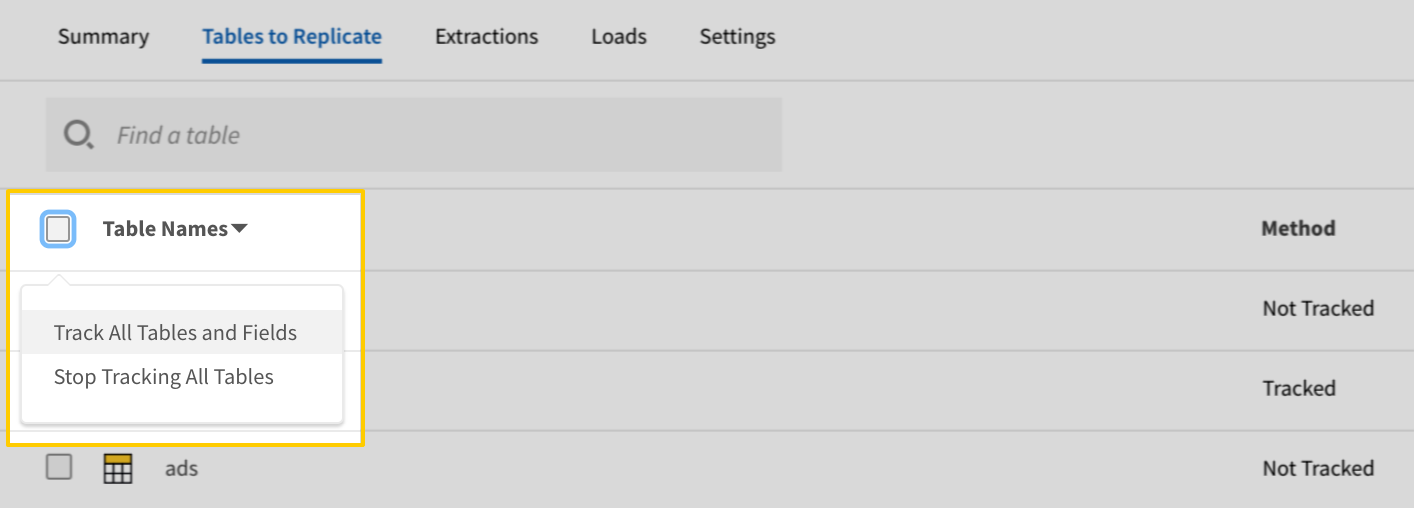
- In the list of tables, click the box next to the Table Names column.
-
In the menu that displays, click Track AllTables and Fields (Except Views):
- Click the Finalize Your Selections button at the bottom of the page to save your data selections.
Setting a database view to replicate is similar to selecting a table, with a few differences. Refer to the Replicating Database Views guide for detailed instructions.
At a high level, you’ll need to complete the following to select a database view:
Initial and historical replication jobs
After you finish setting up Google CloudSQL MySQL, its Sync Status may show as Pending on either the Stitch Dashboard or in the Integration Details page.
For a new integration, a Pending status indicates that Stitch is in the process of scheduling the initial replication job for the integration. This may take some time to complete.
Initial replication jobs with Anchor Scheduling
If using Anchor Scheduling, an initial replication job may not kick off immediately. This depends on the selected Replication Frequency and Anchor Time. Refer to the Anchor Scheduling documentation for more information.
Free historical data loads
The first seven days of replication, beginning when data is first replicated, are free. Rows replicated from the new integration during this time won’t count towards your quota. Stitch offers this as a way of testing new integrations, measuring usage, and ensuring historical data volumes don’t quickly consume your quota.
| Related | Troubleshooting |
Questions? Feedback?
Did this article help? If you have questions or feedback, feel free to submit a pull request with your suggestions, open an issue on GitHub, or reach out to us.